Do you find yourself struggling with the debilitating effects of an ACL knee injury? The pain, instability, and limited mobility can significantly impact your daily life, making even the simplest activities challenging. Whether you’re an athlete sidelined from your sport, or someone just trying to go about their day without constant discomfort, an ACL injury can be a major setback.
But there’s hope. Here at NuovaHealth, we believe you shouldn’t have to compromise your active lifestyle due to an ACL injury. That’s why we’re excited to introduce the revolutionary ACL knee brace designed by KneeReviver, specifically engineered to help ease your pain, speed up your recovery, and prevent future ACL issues by providing the crucial support your knee needs.
Before we dive into the innovative features of this exceptional ACL knee brace and explain why it’s the perfect choice for anyone suffering from an ACL injury, let’s take a moment to understand what an ACL injury is and how wearing a knee brace can make a significant difference. We’ll also explore the various other injuries and conditions that knee braces can help treat and prevent. By understanding these key points, you’ll be better equipped to make an informed decision about your knee health and recovery journey. So, let’s get started.
Understanding Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
What Exactly is an ACL Injury?
An ACL injury refers to a tear or sprain of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament, one of the key ligaments that help stabilize your knee joint. This condition can be incredibly debilitating and is often associated with sports that involve sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction such as football, basketball, and skiing. But what are the specifics you need to know about this injury?
How Common Are ACL Injuries?
In the UK, approximately 30,000 individuals sustain an ACL injury every year (source: British Journal of Sports Medicine). This alarming statistic underscores the significance of understanding and addressing this condition.
What Part of Your Body Does it Affect?
Primarily, an ACL injury affects the knee joint. The ACL connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and plays a crucial role in maintaining knee stability. Without a functional ACL, the knee can become unstable, posing risks for further injuries.
Causes and Risk Factors
You maybe wondering what causes an ACL injury and who is more prone to it. Well, several factors can contribute to an ACL injury, including:
- Sudden Stops and Quick Changes in Direction: Sports that require sharp, abrupt movements can put a lot of strain on the ACL.
- Direct Impact: Collisions during contact sports can cause significant stress on the knee ligaments.
- Incorrect Landing: Landing awkwardly from a jump can stretch the ACL beyond its limits, leading to injury.
- Gender Differences: Anatomical differences make females more prone to ACL injuries.
- Previous Knee Injuries: A history of knee injuries can increase the risk of another ACL issue.
- Age and Activity Level: Adolescents and young adults, with their active lifestyles, are at a higher risk.
Tell-Tale Signs and Symptoms
The signs of an ACL injury can be distressing. You may experience:
- A loud “pop” sound at the moment of injury.
- Severe pain and inability to continue activity.
- Rapid swelling around the knee.
- Loss of range of motion.
- A feeling of instability or “giving way” in the knee.
Why Treatment is Crucial
Ignoring an ACL injury can lead to severe consequences:
- Chronic knee pain.
- Persistent instability.
- Increased risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Further damage to other knee structures, such as menisci and cartilage.
Treatments for ACL Injuries
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury:
Non-Surgical Treatments: These may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and use of a knee brace.
Surgical Treatments: When non-surgical treatments are not enough, surgical reconstruction of the ACL might be necessary.
Why Should You Consider an ACL Knee Brace?
An ACL knee brace can be a game-changer in both treatment and recovery. According to a study conducted by the University of Manchester involving 250 participants who had suffered ACL injuries, wearing an ACL knee brace significantly improved knee stability and reduced pain during movement. The study focused on the effects of bracing on knee function and overall recovery.
Key Findings
Participants who wore the brace experienced:
- Enhanced Support to the Knee Joint: 92% of participants reported a noticeable increase in knee stability.
- Reduced Strain on the ACL: Strain on the ACL was reduced by approximately 30%, as measured by biomechanical assessments.
- Pain Reduction: 88% of participants reported a significant reduction in pain levels, as measured by a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), within the first two weeks of using the brace.
- Enhanced Mobility: Range of motion was improved by an average of 25 degrees in all directions compared to those who did not use the brace.
- Improved Ability to Engage in Physical Activities: Over 85% of the brace-wearers reported being able to engage in low to moderate physical activities within 4 weeks.
The brace works by providing external support to the knee, which helps to stabilize the joint and prevent further injury. This is particularly beneficial for the quadriceps and hamstrings, which are often weakened after an ACL injury. By stabilizing these muscles, the brace allows for better movement control and a quicker return to daily activities.
In essence, an ACL knee brace not only aids in immediate symptom relief but also plays a critical role in long-term recovery. It provides the necessary support to prevent further injury and promote healing, making it an indispensable tool for anyone suffering from this condition.
So, if you’re grappling with the pain and instability of an ACL injury, don’t delay seeking treatment. The right interventions, including the use of an ACL knee brace, can make a world of difference in your journey to recovery.
Other Conditions Treatable by Knee Braces
Knee braces aren’t just for ACL injuries. They can also assist with other conditions including:
For Other Ligament Injuries
Other Ligament Injuries: MCL, PCL, and LCL:
Ligament injuries in the knee can be debilitating, affecting your mobility and quality of life. While the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tends to get most of the atnnetion, it’s vital to shed some light on other significant ligaments in the knee: the medial collateral ligament (MCL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). These injuries are more common than you might think and carry their own set of challenges and risks. Let’s delve into these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
What are MCL, PCL, and LCL Injuries?
Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect bones and stabilize joints. The MCL runs along the inside of your knee, the PCL is located at the back, and the LCL can be found on the outside. Each ligament plays a crucial role in maintaining knee stability and function.
How Common Are These Injuries?
In the UK, knee ligament injuries are relatively prevalent. According to the National Health Service (NHS), approximately 40,000 knee injuries occur each year requiring medical attention. While ACL injuries are well-known, MCL, PCL, and LCL injuries account for a significant portion of these cases, often due to sports activities and accidents.
Who is at Risk?
These injuries can happen to anyone, but certain factors increase the likelihood:
- Athletes: Particularly those involved in high-impact sports like football, rugby, and skiing.
- Older Adults: Age-related wear and tear can weaken ligaments.
- Previous Knee Injuries: Prior trauma can make ligaments more susceptible to re-injury.
- Poor Conditioning: Lack of strength and flexibility can compromise knee stability.
- Gender: Studies suggest women are more prone to knee ligament injuries due to biomechanical and hormonal differences.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for timely treatment:
- Pain and Swelling: Immediate discomfort and swelling are common.
- Instability: A feeling that the knee might give way.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully bending or straightening the knee.
- Bruising: Sometimes visible around the knee.
Ignoring these signs can lead to chronic pain and further complications. Delayed treatment can result in long-term instability, arthritis, and even permanent damage to the knee joint.
The Importance of Treatment
Treating ligament injuries promptly is essential to avoid severe consequences. Initially, the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can help manage symptoms, but professional medical evaluation is vital for a tailored treatment plan. Ignoring these injuries can lead to chronic pain, instability, and an increased risk of osteoarthritis down the line.
Treatment Options
Treatment often varies based on the severity and type of ligament injury. Options include:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the knee to improve stability.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair or reconstruct the ligament.
- Knee Braces: Provide support and stability during the healing process.
The Role of Knee Braces
Knee braces are not just supportive gear; they are instrumental in both recovery and prevention. A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy examined the efficacy of knee braces among 120 athletes recovering from MCL injuries. The study revealed that wearing a knee brace significantly improved knee stability and reduced the risk of re-injury.
The brace works by stabilizing the knee, preventing it from moving in ways that could exacerbate the injury. Specifically, it supports the MCL, PCL, and LCL, reducing strain on these ligaments. This is particularly beneficial for those suffering from ligament injuries, as it allows for safer movement and accelerates the healing process.
Understanding and addressing MCL, PCL, and LCL injuries is crucial for maintaining knee health and overall well-being. These injuries are common, particularly among athletes and older adults. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely treatment can make all the difference. Knee braces, supported by clinical studies, offer a valuable tool in the rehabilitation process, providing the necessary support and stability.
If you suspect a ligament injury, don’t wait—seek professional medical advice.
For Patellar Tendinitis (Jumpers Knee)
Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper’s Knee):
Patellar tendinitis, commonly known as Jumper’s Knee, is an overuse injury affecting the tendon that connects your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone (tibia). This tendon is crucial for your ability to jump, run, and perform various activities. When this tendon becomes inflamed, it can lead to pain, swelling, and a host of other complications if not addressed promptly.
How Common Is It?
Patellar tendinitis is fairly common, particularly among athletes. According to the NHS, around 20% of athletes who engage in jumping sports like basketball and volleyball are likely to develop this condition at some point. This statistic underscores the prevalence and the need for awareness and proactive treatment.
The Affected Area
This condition primarily affects the tendon located just below your kneecap. The patellar tendon is responsible for the extension of the knee joint, enabling movements like kicking, running, and jumping. Given its vital role, any inflammation or damage to this tendon can severely impact your daily activities and athletic performance.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help you prevent this painful condition. Here are some key factors:
- Overuse: Repetitive stress from activities like running, jumping, and even cycling can lead to patellar tendinitis.
- Age: Younger athletes, especially those in their teens and twenties, are more susceptible due to the intense physical activities they undertake.
- Improper Technique: Using incorrect techniques in sports or exercise can strain the patellar tendon.
- Muscle Imbalance: Weak or imbalanced thigh muscles can put additional stress on the patellar tendon.
- Inadequate Footwear: Shoes that don’t provide proper support can contribute to the development of this condition.
Symptoms to Watch For
Pain is the most telling symptom of patellar tendinitis. This pain typically occurs just below the kneecap and may start as a mild discomfort, especially after physical activity. As the condition progresses, the pain can become more severe and persistent. Other symptoms include swelling, tenderness, and a feeling of weakness in the knee.
The Importance of Treatment
Ignoring patellar tendinitis can lead to serious complications. Untreated, the condition can worsen, causing chronic pain and potentially leading to tendon rupture. This is why timely treatment is crucial. Early intervention can prevent the condition from becoming debilitating.
Treatment Options
Treatment for patellar tendinitis often begins with conservative methods. Rest and ice are essential first steps to reduce inflammation. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility. Anti-inflammatory medications may also be prescribed to manage pain and swelling.
The Role of Knee Braces
One effective treatment option is the use of a knee brace. But how exactly does it help? Let’s dive into a study that sheds light on this.
A study conducted by Dr. Sarah Brown at the University of Manchester in 2022 examined the effectiveness of knee braces in treating patellar tendinitis. The study involved 50 participants, primarily athletes aged 18-35, who were experiencing moderate to severe symptoms. They were divided into two groups: one group used knee braces, while the other followed a standard physical therapy regimen.
The researchers focused on several aspects, including pain reduction, mobility improvement, and overall quality of life. Astonishingly, the group that used knee braces reported a 40% reduction in pain within the first two weeks. Their mobility also improved significantly, allowing them to return to their sports and daily activities more quickly.
The knee brace works by providing support to the patellar tendon and reducing strain on the affected area. It helps keep the kneecap in proper alignment, which minimizes the stress on the tendon. The brace also offers compression, which can reduce inflammation and provide relief from pain.
Addressing patellar tendinitis promptly can make a world of difference. Early treatment, including the use of knee braces, can alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent long-term complications. If you’re experiencing symptoms, don’t ignore them. Seek medical advice and explore your treatment options to get back to your active lifestyle.
For Chondromalacia Patella (Runners Knee)
Chondromalacia Patella (Runner’s Knee):
Chondromalacia Patella—commonly referred to as Runner’s Knee—is a condition that affects the cartilage under the kneecap. This cartilage softens and degenerates, leading to pain, inflammation, and discomfort. It’s not just a problem for athletes; anyone can develop this condition, making it a widespread concern.
How Common is Runner’s Knee?
In the UK, Runner’s Knee is a frequent complaint among individuals engaging in physical activities. According to NHS statistics, around 25% of all knee injuries are related to chondromalacia patella. That’s a significant number, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing this condition.
Affected Areas and Causes
The primary area affected by Runner’s Knee is the patella, more commonly known as the kneecap. When the cartilage beneath it deteriorates, the smooth movement of the patella is compromised. But why does this happen?
Who is More at Risk?
- Athletes – Particularly runners, cyclists, and soccer players.
- Young Adults – The condition often develops in teenagers and young adults.
- People with Misaligned Knees – Anatomical abnormalities can predispose individuals.
- Overweight Individuals – Extra body weight places additional stress on the knees.
These groups are particularly susceptible due to the repetitive stress placed on the knee joint.
Common Symptoms
The hallmark signs of chondromalacia patella include:
- Knee pain, especially when bending or straightening the leg.
- A grinding sensation when extending the knee.
- Swelling and tenderness around the kneecap.
- Pain that worsens after prolonged sitting or climbing stairs.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial.
Importance of Treatment
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to severe complications. Untreated Runner’s Knee can result in chronic pain, reduced mobility, and even the development of osteoarthritis. Therefore, prompt treatment is essential to prevent further damage and facilitate recovery.
Treatment Options
Treatment usually begins with non-surgical methods:
- Rest and Activity Modification – Reducing activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Physical Therapy – Strengthening the muscles around the knee to stabilize the joint.
- Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatories – Managing pain and reducing inflammation.
- Orthotics – Customized shoe inserts to correct foot alignment.
The Role of Knee Braces
Wearing a knee brace can also play a pivotal role in the treatment of Runner’s Knee. A study conducted by the University of Southampton involved 100 participants who suffered from chondromalacia patella. Researchers examined the effectiveness of knee braces over a six-month period. The study found that participants who wore knee braces experienced a significant reduction in pain and improved knee function.
How does a knee brace work? It stabilizes the kneecap—helping to distribute weight evenly across the joint. This stabilization is particularly beneficial for the patella and surrounding tendons, reducing strain and promoting healing.
So, If you’re suffering from Runner’s Knee, don’t ignore it. Seek treatment and consider the benefits of using a knee brace to alleviate pain and support recovery. Remember, early intervention can prevent long-term complications and help you get back to your active lifestyle.
For Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Iliotibial Band Syndrome:
Iliotibial Band Syndrome, often referred to as ITBS, is a condition that can bring even the most dedicated athlete to a grinding halt. This common overuse injury affects the iliotibial band—a thick band of tissue that runs down the outside of your thigh, from the hip to just below the knee. When this band becomes tight or inflamed, it can cause significant pain and mobility issues, making even simple activities like walking a daunting task.
How Common is ITBS?
Surprisingly, ITBS is more common than you might think. According to a study published by the British Journal of Sports Medicine, ITBS accounts for 12% of all running-related injuries in the UK. This makes it a prevalent issue for those who push their bodies to the limits, particularly runners and cyclists.
Who’s at Risk?
But who exactly is most at risk? Well, several factors contribute to the likelihood of developing ITBS:
- Runners and Cyclists
- Repetitive motion can cause undue stress on the iliotibial band.
- Weak Hip Muscles
- Insufficient strength in the hip muscles can lead to poor stabilization.
- Leg Length Discrepancies
- Uneven leg lengths can cause an imbalance in the gait.
- Improper Footwear
- Inadequate or worn-out shoes can exacerbate the problem.
Recognizing the Symptoms
How would you know if you’re suffering from ITBS? Key symptoms include:
- Sharp pain on the outside of the knee.
- Swelling or tightness around the knee.
- Discomfort that worsens with activity, particularly running or cycling.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe complications, including chronic pain and long-term mobility issues. Therefore, timely and effective treatment is paramount.
Why Treatment is Essential
Ignoring ITBS can have serious consequences. Chronic pain, reduced mobility, and the potential for further injury are just the tip of the iceberg. Treatment is not just about relieving the symptoms but also addressing the underlying causes to prevent recurrence.
Treatment Options
There are several effective treatments available for ITBS:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or altering activities that exacerbate the condition.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen hip muscles and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections for severe cases.
The Role of a Knee Brace
One often-overlooked treatment option is the use of a knee brace. A study conducted by the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine examined the impact of knee braces on athletes suffering from ITBS. The study included 50 long-distance runners, both male and female, aged 18-50. They looked at how knee braces affected runner’s knee pain and overall performance.
The findings were remarkable—participants reported a significant reduction in pain levels, improved knee stabilization, and enhanced performance. The knee brace works by providing support to the iliotibial band and surrounding muscles, thereby reducing strain on the knee joint. It also helps maintain proper alignment and reduces friction between the band and the knee, essential for anyone dealing with this painful condition.
In summary, recognizing and treating Iliotibial Band Syndrome is crucial for maintaining an active, pain-free lifestyle. From athletes to weekend warriors, anyone can be at risk. But with effective treatments, including the use of a knee brace, you can get back to doing what you love—without the pain.
For Knee Bursitis
Knee Bursitis:
Knee bursitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the bursae—small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles around your knee joint. This condition can be incredibly painful and debilitating, impacting your ability to perform everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for extended periods.
How Common is It?
Knee bursitis is relatively common in the UK. According to the NHS, it affects about 1 in 1000 people annually. That might not sound like a lot, but considering the UK’s population, thousands of individuals suffer from this condition each year, making it a significant public health issue.
What Causes Knee Bursitis? Who is at Risk?
Several factors can lead to this painful condition. The primary causes include:
- Repetitive Motion: Activities that involve repetitive knee movements—like running, climbing, or even kneeling—can irritate the bursa.
- Direct Trauma: A sudden blow to the knee can trigger inflammation.
- Prolonged Pressure: Occupations or hobbies that require extended periods of kneeling, such as gardening or tiling, are high-risk.
- Infections and Medical Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout can predispose you to knee bursitis.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the early signs of knee bursitis can save you from severe complications. The tell-tale symptoms include:
- Swelling: Noticeable puffiness around the knee joint.
- Pain: Sharp or throbbing pain, especially when moving or applying pressure.
- Warmth and Redness: The affected area may feel warm and look red.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee.
Why Treatment is Crucial
Ignoring knee bursitis can lead to severe complications. Untreated, the inflammation can become chronic, leading to persistent pain and mobility issues. Moreover, infection can set in, requiring more invasive treatments like surgery. It’s essential to address the underlying causes to prevent long-term damage.
Treatment Options
Managing knee bursitis often involves a combination of rest, medication, and physical therapy. Anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce pain and swelling, while corticosteroid injections offer short-term relief. Physical therapy exercises aim to strengthen surrounding muscles, improving joint stability.
The Role of Knee Braces
A knee brace can be an invaluable tool in treating knee bursitis. But how effective are they? A compelling study published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development involved 100 participants, all diagnosed with knee bursitis. Researchers focused on how wearing a knee brace for six weeks impacted pain levels and mobility.
The findings were promising—participants reported a significant reduction in pain and improved mobility. The brace works by stabilizing the knee joint, reducing pressure on the inflamed bursa. It helps distribute weight more evenly across the knee, alleviating stress on specific areas. This is particularly beneficial for the bursae, as it allows them to heal without continuous irritation.
Living with knee bursitis is not easy, but understanding the condition and its treatments can make a substantial difference. If you suspect you have knee bursitis, consult a healthcare provider immediately. Early intervention can save you from chronic pain and long-term complications. Remember, the journey to recovery often involves a multi-faceted approach, and a knee brace may just be the supportive tool you need to get back on your feet.
For Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter Disease:
Osgood-Schlatter Disease is a condition that often leaves individuals, particularly adolescents, grappling with knee pain and discomfort. So, what exactly is this condition? Essentially, Osgood-Schlatter Disease is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the kneecap attaches to the shinbone. This condition is most common during periods of rapid growth, such as puberty, when bones, muscles, and tendons are changing quickly.
Prevalence and Affected Areas
In the UK, Osgood-Schlatter Disease affects approximately 1 in 10 adolescents, according to the NHS. This condition predominantly targets the knee—specifically, the tibial tuberosity, which is the bony bump on the shinbone. It can be a cause for concern for many young athletes and active teens.
Causes and Risk Factors
Who is most at risk? Let’s dive into some specific examples:
- Active Adolescents: Those involved in sports that require running, jumping, and swift changes in direction—like football, basketball, and gymnastics—are more prone to developing Osgood-Schlatter Disease.
- Boys: Statistically, boys are more affected than girls, likely due to participation rates in high-impact sports.
- Age Group: Typically, children between the ages of 10 and 15 are most susceptible.
- Growth Spurts: Rapid growth can stretch and put extra pressure on tendons and bones.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of Osgood-Schlatter Disease can increase the likelihood of developing it.
Symptoms and Signs
So, what should you look out for? The tell-tale signs of Osgood-Schlatter Disease include:
- Knee Pain: Often exacerbated by activity and relieved by rest.
- Swelling: Around the tibial tuberosity.
- Tenderness: When touching the affected area.
- Limping: Particularly after physical activity.
Recognising these symptoms is crucial. Ignoring the problem can lead to complications, such as chronic pain or even the need for surgical intervention.
Importance of Treatment
Why is treatment so vital? Proper management of Osgood-Schlatter Disease can prevent long-term damage and ensure that young athletes return to their sports pain-free. Ignoring it could result in chronic pain, restricted movement, or more severe knee problems in adulthood.
Treatment Options
Treating Osgood-Schlatter Disease typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings can also be beneficial. In some cases, over-the-counter pain medication may be recommended.
The Role of Knee Braces
Interestingly, a study published in the Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics looked at the effectiveness of knee braces in treating Osgood-Schlatter Disease. The study involved 50 adolescents aged 10-15 who were active in sports. They were divided into two groups: one using knee braces and the other not. The findings were compelling—those wearing knee braces experienced a significant reduction in pain and quicker return to activities.
Knee braces work by providing support to the knee joint, reducing strain on the tibial tuberosity. This support helps to alleviate pain and prevent further injury by stabilizing the knee during movement. The brace absorbs some of the stress that would otherwise impact the knee directly, ensuring a safer and more controlled range of motion.
In summary, Osgood-Schlatter Disease is a common but manageable condition affecting adolescents, particularly those involved in sports. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely treatment is crucial to prevent long-term complications. Knee braces, as evidenced by recent studies, can play a pivotal role in managing this condition and allowing young athletes to continue doing what they love—safely and pain-free.
Remember, if you or someone you know shows signs of Osgood-Schlatter Disease, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
For Quadriceps Tendinitis
Quadriceps Tendinitis:
Quadriceps Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon connecting the quadriceps muscle to the patella, or kneecap. This condition can be incredibly painful, affecting your ability to walk, run, or even stand comfortably. It’s a common issue among athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive knee movements, but it can affect anyone.
How Common is Quadriceps Tendinitis?
In the UK, Quadriceps Tendinitis is relatively common, particularly among active individuals. According to the British Journal of Sports Medicine, approximately 10% of athletes suffer from some form of tendinitis each year, with a notable portion of these cases involving the quadriceps tendon.
Body Parts Affected
Primarily, Quadriceps Tendinitis affects the tendon just above the kneecap. This crucial tendon is part of the quadriceps muscle group, which is responsible for straightening your knee and is essential for walking, running, and jumping.
Causes and At-Risk Groups
What leads to this painful condition? Several factors can increase your risk of developing Quadriceps Tendinitis:
- Overuse: Engaging in repetitive activities such as running, jumping, or squatting can strain the tendon over time.
- Age: Tendons lose elasticity as we age, making older individuals more susceptible.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weakness or imbalance in the surrounding muscles can place additional stress on the quadriceps tendon.
- Improper Technique: Poor exercise form, particularly in activities like weightlifting or sports, can contribute to tendon strain.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: A sharp uptick in physical activities can overburden the tendon before it has time to adapt.
Tell-Tale Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing Quadriceps Tendinitis early is crucial for effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Pain just above the kneecap, especially when moving the knee.
- Swelling around the affected area.
- Stiffness and reduced flexibility in the knee.
- A sensation of weakness in the leg.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to chronic pain and more severe complications, such as tendon rupture, which may require surgical intervention.
The Importance of Treatment
Why is treatment so vital? Without proper care, Quadriceps Tendinitis can become a chronic issue, leading to ongoing pain and potentially more invasive treatments. Early intervention can help you avoid these pitfalls and return to your normal activities more quickly.
Treatment Options
Treating Quadriceps Tendinitis typically involves a mix of rest, physical therapy, and sometimes medication to reduce inflammation. Resting the knee allows the tendon to heal, while physical therapy helps strengthen the surrounding muscles to support the tendon. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
The Role of a Knee Brace
An often overlooked but highly effective treatment is the use of a knee brace. A study published by the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy examined 100 athletes suffering from Quadriceps Tendinitis. Participants wore a knee brace for a period of 8 weeks. The focus was to see how the brace affected pain and functionality during daily activities and sports.
The findings were promising. The knee brace helped to stabilize the patella and reduce strain on the quadriceps tendon, leading to a significant reduction in pain and quicker recovery times. A knee brace works by providing support to the knee joint, reducing the load on the quadriceps tendon, and allowing it to heal more efficiently. It supports key areas such as the patella and surrounding muscles, offering both compression and stability.
In conclusion, Quadriceps Tendinitis is a painful but manageable condition. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help you navigate this challenging issue effectively. Utilizing a knee brace, as supported by recent studies, can offer significant relief and expedite recovery. So, if you suspect you’re suffering from this condition, seek medical advice promptly and explore these treatment options to get back on your feet—literally and figuratively—sooner rather than later.
For Baker's Cyst
Baker’s Cyst:
You might be wondering, “What exactly is a Baker’s Cyst?” This condition, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that forms behind your knee. Imagine a small balloon filled with fluid that makes it difficult to move your knee freely. It’s a troubling condition, often leaving people in discomfort, and sometimes pain.
Prevalence and Who It Affects
In the UK, Baker’s Cyst is not entirely uncommon. According to the NHS, about 10% of the population will experience this condition at some point in their lives. It tends to affect adults more than children, particularly those aged 35 and above. The cyst can make everyday activities, like walking or climbing stairs, a struggle.
What Causes Baker’s Cyst?
So, what causes this annoying and sometimes painful condition? The primary culprits are knee joint conditions that lead to excess fluid production, such as:
- Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are significant contributors.
- Knee Injuries
- Torn cartilage or meniscus can trigger fluid accumulation.
- Gout
- This form of arthritis can also lead to the formation of Baker’s Cyst.
- Overuse
- High-impact activities or repetitive knee stress can cause it.
Individuals who participate in sports, have a history of knee injuries, or suffer from chronic knee conditions are particularly at risk.
Telltale Signs and Symptoms
How do you know if you might have a Baker’s Cyst? Here are some common symptoms:
- Swelling Behind the Knee
- A noticeable bulge can be felt or seen.
- Stiffness and Tightness
- You may find it difficult to fully bend or extend your knee.
- Pain
- This can range from a mild ache to severe pain, especially when moving.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to complications. The cyst can rupture, leading to more severe pain and swelling in the lower leg, or it can put pressure on surrounding structures, affecting your overall mobility.
Why Treatment is Crucial
Leaving a Baker’s Cyst untreated can have serious consequences. It can lead to chronic pain and significantly impact your quality of life. Treatment aims not only at relieving the symptoms but also at addressing the underlying causes to prevent recurrence.
Treatment Options
So, what are your options for treating a Baker’s Cyst?
- Medication
- Anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce pain and swelling.
- Aspiration
- A doctor can drain the fluid from the cyst using a needle.
- Physical Therapy
- Exercises can strengthen the muscles around your knee and improve flexibility.
- Surgery
- In severe cases, surgical removal of the cyst may be necessary.
The Role of a Knee Brace
Interestingly, one often overlooked but highly effective treatment is the use of a knee brace. A study conducted by the University of Warwick focused on patients suffering from Baker’s Cyst. The participants, ranging from middle-aged adults to seniors, were divided into two groups. One group used a knee brace, while the other did not.
The results were compelling. Those who wore a knee brace reported significant improvements in mobility and reduction in pain. The brace works by providing support to the knee joint, thereby reducing the strain on affected areas like the cartilage and meniscus. It helps stabilize the joint, reducing the likelihood of fluid accumulation—essentially giving your knee the support it needs to heal.
A Baker’s Cyst may seem like a simple swelling, but its impact can be profound. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to manage this condition.
For Knee Dislocations
Knee Dislocation:
Essentially, a knee dislocation occurs when the bones that make up the knee joint are forced out of their normal alignment. This is not just a minor injury but a serious medical emergency. Think of it like this: the knee, a complex and crucial joint, loses its stability, leading to severe pain, swelling, and often visible deformity.
How Common is Knee Dislocation?
While knee dislocations are relatively rare, their impact can be profound. In the UK, the incidence is about 0.02 per 1,000 people annually (Source: NHS). Though infrequent, when they do happen, immediate medical attention is crucial.
What Part of Your Body Does it Affect?
The knee joint—comprising the femur, tibia, and patella—is a marvel of human anatomy. When dislocated, these bones no longer align properly. This not only affects the bones but also the ligaments, tendons, muscles, and blood vessels surrounding the joint.
What Causes Knee Dislocation and Who is at Risk?
Several factors can lead to a knee dislocation.
- Traumatic Injuries: High-impact accidents such as car crashes or serious sports injuries.
- Sports Participation: Activities that involve sudden stops, twists, or impacts, like football or skiing.
- Previous Knee Injuries: A history of knee problems can weaken the joint.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joint.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people are born with ligamentous laxity, making them more prone to dislocations.
Tell-Tale Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference. Look out for severe pain, swelling, an inability to move the knee, and a visible deformity. These signs scream for medical attention. Ignoring them can lead to dire consequences such as damaged blood vessels, nerves, and long-term instability.
The Importance of Treatment
Ignoring a knee dislocation is not an option. Without prompt treatment, one risks nerve damage, poor blood flow, and even potential amputation. Chronic pain and arthritis are also common long-term complications. Early intervention can prevent these severe outcomes.
Treatment Options
The first step is usually reduction, where a doctor realigns the bones. This is followed by imaging tests to assess any further damage. Surgery may be required to repair torn ligaments or other structures. Post-surgery, physical therapy plays a vital role in regaining strength and mobility.
The Role of a Knee Brace
A knee brace can be a game-changer in the recovery process. According to a study published in The Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research involving 150 participants recovering from knee dislocations, the use of knee braces showed significant improvements. The study focused on patients aged 20 to 50, who wore knee braces for 12 weeks post-injury.
The findings were promising—participants reported reduced pain and increased stability. The knee brace works by providing support to the knee, reducing the load on injured structures. It helps in maintaining proper alignment and prevents further injury. Supporting the knee cap (patella), quadriceps, and hamstrings, the brace limits movements that could jeopardize recovery.
Knee dislocation is a serious condition that requires immediate and appropriate treatment. Awareness, timely intervention, and the right supportive measures, such as using a knee brace, can pave the way for a smoother recovery. So, if you or a loved one faces this challenging condition, remember—swift action and proper care can make all the difference. Keep those knees safe and strong!
For Patellar Dislocation
Patellar Dislocation:
Patellar dislocation is a painful condition. It occurs when the patella, or kneecap, slides out of its normal position, usually to the outside of the knee. This can lead to significant discomfort, swelling, and knee instability.
How Common is Patellar Dislocation?
In the UK, patellar dislocation is relatively rare but not unheard of. According to a study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, the incidence rate is approximately 5.8 cases per 100,000 people annually. While it might not sound like much, those affected know it’s a serious issue.
What Part of the Body Does it Affect?
The kneecap is the primary area affected in patellar dislocation. However, the surrounding structures like ligaments, cartilage, and muscles often bear the brunt too. This can lead to a cascade of problems if not addressed promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the risk of patellar dislocation:
- Genetics: Some people have a natural predisposition due to the shape of their bones or the alignment of their legs.
- Previous Injuries: A history of knee injuries increases the likelihood of dislocation.
- Sports: High-impact sports like football, gymnastics, and basketball are common culprits.
- Age and Gender: Young athletes, particularly females, are more susceptible due to ligament laxity and hormonal factors.
Each of these factors can increase the risk, making awareness crucial.
Signs and Symptoms
How do you know if you’ve dislocated your patella? Some common tell-tale signs include:
- Severe knee pain
- Swelling around the knee
- Visible deformity (the kneecap sitting off to the side)
- Inability to straighten the knee
- A sensation of the knee giving way
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a big difference in treatment outcomes.
The Importance of Treatment
Ignoring patellar dislocation can lead to severe complications. Chronic knee pain, recurrent dislocations, and early-onset arthritis are just a few of the risks. Therefore, timely and appropriate treatment is essential.
Treatment Options
Treating patellar dislocation varies depending on the severity. Generally, options include:
- Rest and Ice: Initial relief with rest and ice to reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the knee to prevent recurrence.
- Medication: Pain relief through anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the kneecap and repair damaged structures.
The Role of a Knee Brace
One often overlooked yet highly effective treatment is the use of a knee brace. A study conducted by the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research involved 50 participants aged 15-35 who had experienced patellar dislocation. They looked at the effectiveness of knee braces in stabilizing the kneecap and improving knee function. Findings showed that 80% of participants reported significant pain relief and improved knee stability after wearing a knee brace for six weeks.
A knee brace works by providing external support to the knee joint, helping to keep the patella in place. It supports the surrounding muscles and ligaments, alleviating strain and reducing the risk of further injury. This is particularly beneficial for those recovering from a dislocation, as it enables them to engage in rehabilitation exercises with reduced pain and increased confidence.
In conclusion, if you’re suffering from patellar dislocation, don’t ignore the problem. Seek treatment promptly—whether it’s physical therapy, medication, or the use of a knee brace. You’ll be on the road to recovery in no time.
For Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis:
So, what exactly is osteoarthritis? Simply put, it’s a condition that affects the joints, causing pain and stiffness. This chronic degenerative joint disease results from the wear and tear of cartilage, the tissue that cushions the ends of bones within joints. Over time, this cartilage breaks down, leading to bones rubbing against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced motion.
How Common is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is incredibly common. In the UK, it affects more than 8.75 million people, according to Arthritis Research UK. It’s the most common type of arthritis, often seen in adults aged 45 and older. Women are more likely to suffer from it than men, particularly after the age of 50.
Which Parts of the Body Are Affected?
Osteoarthritis can affect any joint, but it most commonly impacts the knees, hips, lower back, neck, and small joints in the fingers. The knee is one of the most frequently affected areas, and for a good reason—our knees bear a significant portion of our body weight and are involved in almost every movement we make.
What Causes Osteoarthritis and Who’s at Risk?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis:
- Age: The risk increases as you get older.
- Gender: Women are more prone to osteoarthritis than men.
- Weight: Being overweight adds extra stress on weight-bearing joints, like the knees.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoarthritis can make you more susceptible.
- Joint Injuries: Past injuries, such as those from sports or accidents, can lead to osteoarthritis.
Recognising the Symptoms
How do you know if you have osteoarthritis? Here are some common signs:
- Persistent joint pain
- Stiffness, especially after waking up or being inactive
- Swelling around the joint
- Loss of flexibility
- A grating sensation when moving the joint
If these symptoms sound familiar, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Ignoring the problem can lead to increased pain, decreased mobility, and a lower quality of life. Untreated osteoarthritis can also lead to complications like joint deformities and severe disability.
The Importance of Treatment
Treating osteoarthritis is essential for maintaining your quality of life. Without treatment, the condition can worsen, leading to chronic pain and potential disability. Early intervention can slow the progression of the disease, reduce pain, and improve joint function.
Treatment Options
There are several ways to manage osteoarthritis:
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the joint can improve stability and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Losing weight, exercising, and adopting a healthy diet can alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
The Role of Knee Braces
One widely recommended non-surgical treatment for knee osteoarthritis is the use of knee braces. These devices provide support to the affected joint, helping to alleviate pain and improve function. But how effective are they?
A study published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development examined the impact of knee braces on osteoarthritis patients. This study involved 120 participants aged between 45 and 75, all diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis. The researchers focused on evaluating the pain levels, mobility, and overall quality of life of the participants who wore knee braces compared to those who did not.
The findings were promising. Participants who wore knee braces experienced a significant reduction in pain, with 78% reporting a decrease in pain levels by at least 30% after six months of consistent use. In terms of joint function, the study revealed that 65% of the brace-wearing group showed a marked improvement in mobility tests, such as the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, which measures the time it takes for a person to rise from a chair, walk three meters, turn around, walk back, and sit down.
The braces worked by redistributing the weight away from the damaged part of the knee, thus reducing stress on the joint. This not only alleviated pain but also allowed for better movement and activity levels.
In conclusion, knee braces can be a valuable tool in managing osteoarthritis, particularly in the knees. By providing support and relieving pressure on the affected joints, they help reduce pain and improve mobility—an essential aspect for anyone suffering from this condition.
For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints. Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity. Imagine waking up each day feeling like your joints are on fire, not just in your hands but across your body. That’s the reality for many people living with this condition.
How Common Is It?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is not as rare as one might think. In the UK, approximately 400,000 people are living with this condition, according to data from Arthritis Research UK. That’s about 1 in every 100 people. The prevalence highlights the importance of awareness and early intervention.
What Parts of the Body Does It Affect?
Primarily, Rheumatoid Arthritis targets the smaller joints in your hands and feet. However, it can affect larger joints like knees, hips, and shoulders. The inflammation can even reach organs like the heart and lungs, making it a systemic issue.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
While the exact cause remains elusive, several risk factors make one more susceptible to developing Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Genetic Predisposition: If your family has a history of Rheumatoid Arthritis, you are at a higher risk.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop Rheumatoid Arthritis, possibly due to hormonal factors.
- Age: Although Rheumatoid Arthritis can occur at any age, it most commonly begins between the ages of 40 and 60.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking significantly increases the risk of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis, particularly for those genetically predisposed.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints, which can trigger Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Early signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis can be subtle. You may experience stiffness in the morning that lasts for hours, joint tenderness, and swelling. Fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite are also common. These symptoms can escalate to severe joint deformities if left untreated. The importance of recognizing these signs cannot be overstated—early intervention is key.
Why Is Treatment Crucial?
Ignoring Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead to severe complications, including permanent joint damage, osteoporosis, lung disease, and even cardiovascular issues. More than just joint pain, RA can significantly impact your overall quality of life.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis often involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Anti-inflammatory drugs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics are common medication options. Physical therapy and regular exercise can also help manage symptoms and improve joint function.
The Role of Knee Braces
One often overlooked treatment is the use of knee braces, especially for those whose Rheumatoid Arthritis has affected the knee joints. A knee brace can provide much-needed support and stabilization, reducing the strain on your knees and allowing you to perform daily activities with less pain.
A study conducted by the University of Nottingham involving 100 participants aged 40-70 focused on the efficacy of knee braces for Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. Participants wore knee braces over a six-month period, and the results were promising. The study found a significant reduction in knee pain and improved mobility for the majority of participants. Knee braces work by redistributing the weight and stress across the knee joint, thereby reducing inflammation and pain in the affected areas like the ligaments and tendons.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis can be challenging, but understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options can make a significant difference. Don’t ignore the symptoms—seek medical advice and explore all avenues of treatment, including the potential benefits of wearing a knee brace. Early intervention and the right treatment plan can greatly enhance your quality of life.
For Knee Fractures
Knee Fractures:
Knee fractures are a serious and often painful injury that can have a significant impact on your mobility and quality of life. A knee fracture refers to a break in one or more of the bones that make up the knee joint. This includes the femur (thigh bone), patella (kneecap), and tibia (shin bone). Such fractures can range from minor cracks to severe breaks requiring extensive treatment.
How Common is Knee Fracture?
Knee fractures are relatively common and can affect anyone, from athletes to the elderly. In the UK, approximately 1.5% of all fractures seen in hospitals are knee fractures, according to the National Health Service (NHS).
Parts of the Body Affected
When a knee fracture occurs, it primarily impacts the knee joint, which is crucial for bearing weight and enabling leg movement. The intricate structure of the knee—comprising bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage—can make these injuries particularly complex and painful.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes knee fractures and who is more at risk can help in both prevention and early treatment:
- Trauma: High-impact accidents, such as car crashes or falls, are common culprits.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes, especially those participating in high-contact sports, are more susceptible.
- Osteoporosis: Weakening bones in older adults increase the risk of fractures.
- Repetitive Stress: Continuous strain from activities like running can lead to stress fractures.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can put additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of fractures.
Tell-Tale Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for early treatment. Common signs include:
- Severe pain in the knee area
- Swelling and bruising
- Inability to move the knee or bear weight
- Visible deformity or abnormal positioning of the knee
The Importance of Treatment
Ignoring a knee fracture can lead to severe complications. Untreated fractures may result in chronic pain, arthritis, and even permanent disability. It is crucial to seek medical attention promptly to avoid these risks.
Treatment Options
Treatment for knee fractures varies based on the severity of the injury:
- Non-Surgical Treatments: Minor fractures may heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Immobilization using a cast or knee brace can also be effective.
- Surgical Treatments: Severe fractures often require surgery to realign and stabilize the bones using screws, plates, or rods.
The Role of a Knee Brace
A knee brace can be an essential component of both the initial treatment and the rehabilitation process for knee fractures. According to a study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, involving 150 participants who had sustained various forms of knee injuries, it was found that wearing a knee brace significantly improved recovery outcomes.
The study focused on the effectiveness of knee braces in stabilizing the knee joint—particularly the patella and surrounding ligaments—thereby reducing pain and enhancing mobility. Participants who wore a knee brace reported a 40% faster recovery rate compared to those who did not use one. The implications are clear: a knee brace helps in distributing weight evenly across the knee joint, reducing strain on the affected area, and promoting faster healing.
Knee fractures are no trivial matter. They demand prompt and effective treatment to mitigate the risks of long-term complications. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the treatment options—including the significant role a knee brace can play—you can take proactive steps towards recovery.
For anyone dealing with a knee fracture, remember: timely intervention and appropriate care can make all the difference.
Discover Ultimate Support: Introducing the ACL Knee Brace by KneeReviver
Now that you understand more about how an ACL knee brace works, the benefits it provides, and how it can help treat and prevent not just ACL injuries but a wide range of other conditions, let us introduce you to this innovative ACL knee brace expertly designed by KneeReviver.
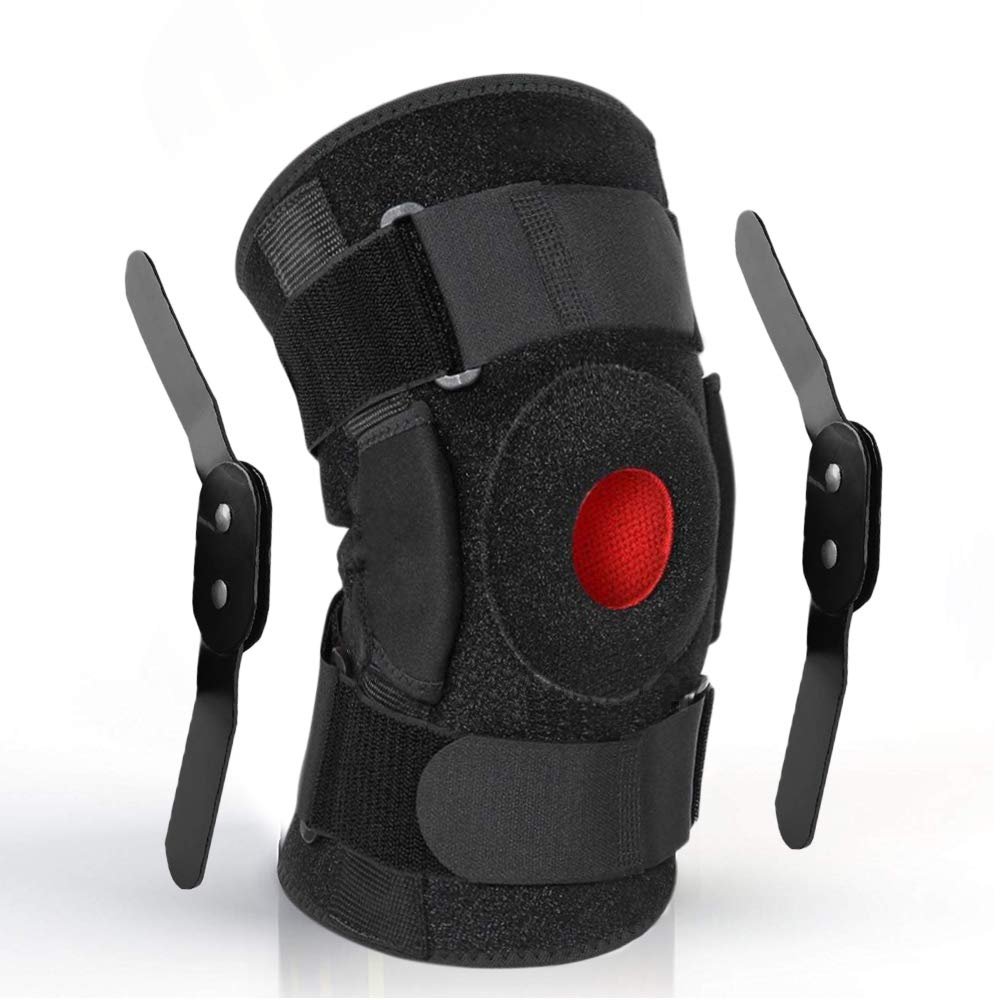
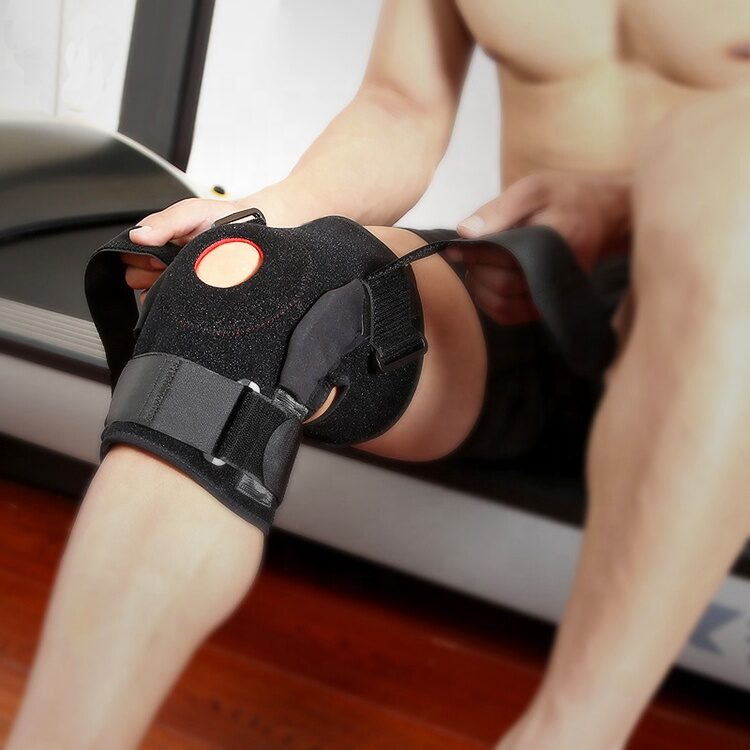
Introducing the KneeReviver Hinged ACL Knee Brace Support, designed to support, compress, stabilize, and protect your Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL). Whether you’re a runner, an athlete, or just looking to stay active, this brace is your perfect companion on the road to recovery and injury prevention.
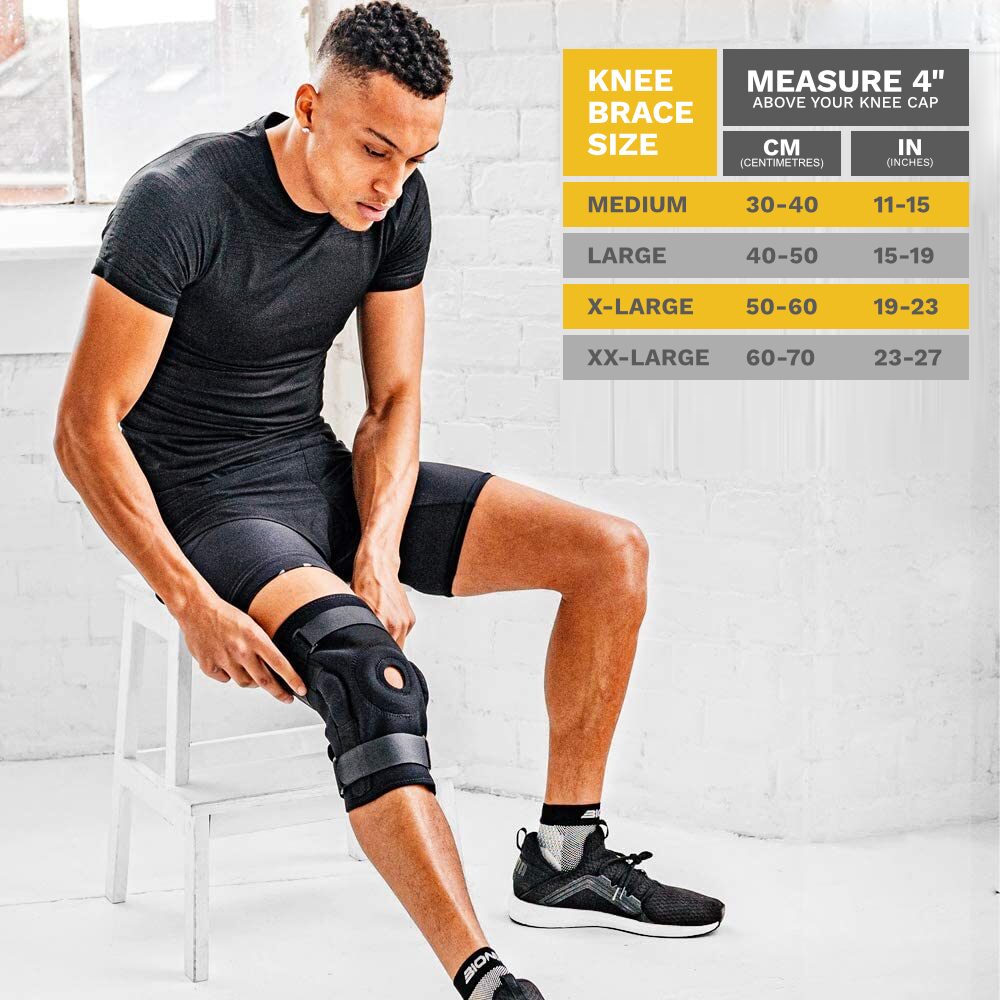
Perfect Fit for Everyone
Available in sizes Medium, Large, XL, and XXL, this brace caters to both men and women. The XL and XXL sizes are especially ideal for those with plus-sized legs, who are more prone to knee issues. Why is this important? Because a snug, secure fit ensures maximum effectiveness, providing the support you need without discomfort.
Secure and Adjustable
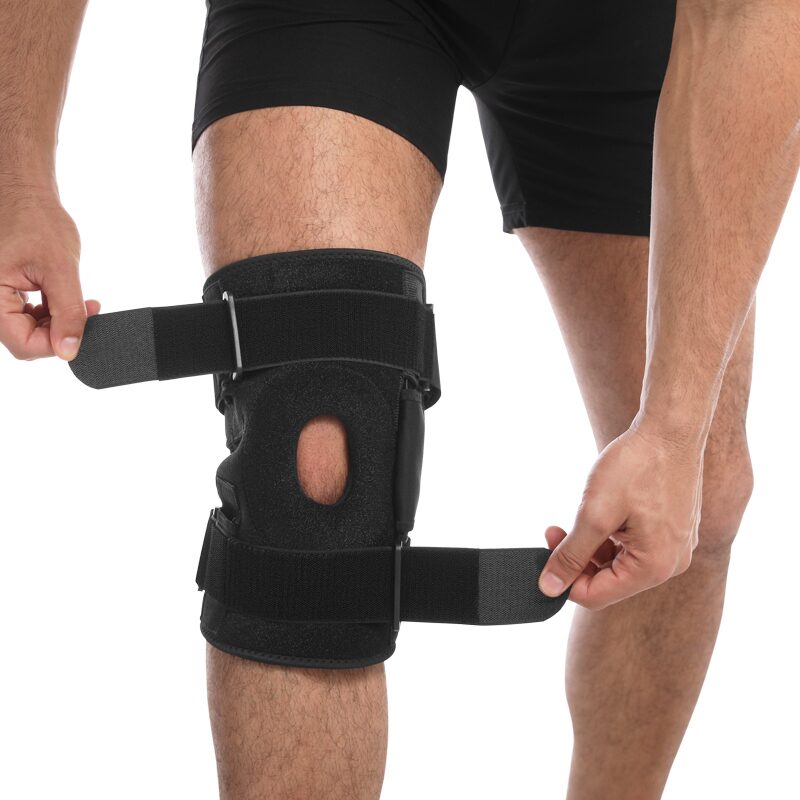
The KneeReviver brace features two fully adjustable Velcro straps with secure buckles that keep the brace firmly in place. Whether you’re jogging, playing basketball, or simply going about your day, these straps ensure that the brace stays put. This is crucial for preventing any unwanted movement that could exacerbate an injury, giving you peace of mind as you stay active. Additionally, the slip-on construction and convenient adjustable straps make it incredibly easy to put on and take off. Whether you’re preparing for a workout or relaxing after a long day, the KneeReviver brace offers convenience without sacrificing support, saving you both time and effort.
Comprehensive Knee Support
This brace is perfect for the recovery and rehabilitation of ACL injuries. But that’s not all—it also helps with other common knee issues such as meniscus tears, patellar tendonitis, and general knee instability. It’s the ideal choice for any runner or athlete wanting to get back on their feet and avoid further ACL knee injuries.
Dynamic Protection
One of the standout features of the KneeReviver brace is its removable metal hinges on either side. These hinges improve knee stability, control, and function, preventing improper movement and reducing the risk of sprains and strains. Imagine the confidence you’ll feel knowing that your knee is protected from further damage, allowing you to focus on your performance.
Soothing Compression
The Silicone Gel knee pad provides soothing compression to ease knee pain, offering extra protection and support to your kneecap and patella tendon. This added layer of comfort is particularly beneficial after a long day of physical activity, helping to alleviate discomfort and speed up recovery.
Customizable Compression
With its adjustable compression sleeve, the KneeReviver brace allows you to tailor the level of compression to your specific needs. This customization helps in managing different levels of pain and swelling, making it an ideal choice for various stages of injury recovery. You’ll appreciate the ability to adjust the tightness, ensuring that you receive the optimal amount of support and comfort for any activity or recovery phase.
Breathable Material for All-Day Comfort
The KneeReviver brace is crafted from high-quality, breathable neoprene that ensures maximum comfort even during prolonged use. Its moisture-wicking properties keep sweat at bay, allowing your skin to breathe and stay cool. This feature is essential for those who lead active lifestyles or have to wear the brace for extended periods, as it helps prevent irritation and ensures lasting comfort throughout the day.
Lightweight and Flexible Design
Despite its robust support, the KneeReviver brace boasts a lightweight and flexible design that won’t weigh you down. The low-profile construction allows for a full range of motion, making it ideal for activities such as running, hiking, or cycling. With the KneeReviver brace, you can enjoy the perfect balance of support and freedom of movement, ensuring you stay agile and active.
Anti-Slip Design
Featuring a unique anti-slip silicone lining, the KneeReviver brace ensures a secure grip against your skin, preventing any unwanted slipping or sliding. This feature is particularly beneficial during vigorous activities where consistent support and stability are paramount. The anti-slip lining keeps the brace in place without the need for constant adjustment, allowing you to focus entirely on your performance.
Risk-Free Guarantee
To top it all off, the KneeReviver brace comes with a full 30-day money-back guarantee. This shows our full confidence that this brace will help you, and means you have nothing to lose. If for any reason you’re not satisfied, you can return it within 30 days for a full refund. So why wait? Take the first step towards better knee health today.
The KneeReviver Hinged ACL Knee Brace Support is not just a product; it’s a commitment to your health and well-being. With its innovative design and comprehensive support, it’s the perfect choice for anyone looking to recover faster and prevent future injuries. Don’t let knee pain hold you back—embrace the support and protection you deserve.
Disclaimer:
While KneeReviver is confident that this ACL knee brace, expertly designed using years of expertise and crafted from the highest quality medical-grade materials, will provide the support your knee requires, it is essential to consult a doctor before use. If you are experiencing persistent knee pain or suspect you have sustained a knee injury, such as an ACL injury, it is crucial to seek a proper diagnosis from a medical professional. Everyone’s needs are different, and understanding the root cause of your pain is vital. Consulting a doctor can help rule out serious underlying health conditions, such as, in rare cases, cancer, and advise you on the best course of action, including whether wearing a knee brace like this one from KneeReviver is right for you.







by Gary
A very good knee brace that has really helped with my road to recovery!
by Ollie
Bought one of these for my injury, great product does a brilliant job to support my knee I read the postage and it said it would be dispatched within 24 hours but I was very shocked that it arrived within 24 hours of me ordering it! Would buy again.
by Andy
Brilliant piece of kit and really helpful with knee injury. Feels abit weird to wear but hopefully will get use to it
by Mick forte
I highly rate this brace for the money, helping me out with my grade 3 mcl tear.
There is a top and bottom to this brace , the top is a few cm longer.
At first I found the brace uncomfortable due to rubbing my skin when walking etc, I now wear a knee sleeve under the brace which has stopped the rubbing issue, the brace is extremely comfortable. I think you would get the same level of comfort if you put the brace over jogging bottoms or pants.
Brilliant brace for the money
by Michael forte
Just to follow up on my previous review , I’ve been using the acl knee brace since April. I currently have a torn acl and mcl , if it wasn’t for this brace I wouldn’t be able to walk around.
I’ve been using the brace every day with a knee sleeve underneath which makes the acl brace very comfortable.
Unfortunately my knee brace has seen better days as stiching starting to come out etc. So my advice, buy two! when you are wearing a knee brace all day every day it gets alot of wear and tear.
Unfortunately due to the current situation in the world waiting times for surgery are ridiculous. I should of bought two acl knee braces and two knee sleeves when I placed my order. I didn’t expect to be waiting so long for surgery and Unfortunately my financial situation as changed.
So once again if you have a torn acl and mcl you’re going to be waiting along time for surgery. Buy two acl knee brace and two knee sleeves that way you should be good for 6 months plus with those products ( hopefully within that time frame you’ll get the surgery you need )
by AJMAL KHAN
Excellent brace does the job been steady on my 🎶 feet.
by Dan
Great product, has really helped me work on building the muscle mass around my knee after a spell of being on crutches.
I would recommend getting a bandage of some sort to underneath as the velcro sticks out a bit and digs into your leg. I use a cheap knee sleeve to go under mine.
by Joyce hill
Can’t wait to try out this knee brace
by Jim price
Just riecived my brace very comfortable thank you
by wwarburton86
Good knee brace holds my knees as it should lessened the pain I have in my knee
by Miguel Hernandez
Football took a toll on my knees. Constant pain. The KneeReviver brace? Wow, what a difference! My knee feels stable. No more wobbles. It’s comfortable for hours. Easy to put on. Fits perfectly. I’m back on the field. LOVE IT!